Know More answers
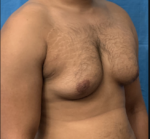
WHAT ARE MALE BREASTS / GYNECOMASTIA / MAN BOOBS?
Male breasts, also known medically as gynecomastia (guy-ne-co-mas-tee-uh) or informally as “man boobs”, refer to the enlargement of breast tissue in males. It’s a relatively common condition, affecting up to 65% of men at some point in their lives, though not all cases are noticeable.
Gynecomastia is caused by an imbalance of hormones, specifically estrogen and testosterone. In males, testosterone is the dominant sex hormone, and estrogen is present at much lower levels. When this balance is disrupted, with estrogen levels rising or testosterone levels dropping, breast tissue growth can be stimulated.
-
Physiological gynecomastia: This is a normal occurrence during certain stages of a man’s life
-
Newborn babies: Up to 90% of newborns experience breast enlargement due to exposure to maternal hormones during pregnancy.It typically resolves on its own within a few weeks.
-
Puberty: During puberty, hormonal fluctuations can cause breast tissue development in teenage boys. This usually resolves within 6 months to 2 years.
-
Older adults: As men age, testosterone production naturally declines,which can lead to gynecomastia.
-
Pathological gynecomastia: This type of gynecomastia is caused by an underlying medical condition, medication use, or other factors.
WHEN TO GET MALE BREAST REDUCTION SURGERY?
There isn’t a one-size-fits-all answer to when to get male breast reduction surgery (gynecomastia surgery). Here are some factors to consider that might indicate it’s a good time for you:
-
Your breasts have finished developing: Ideally, wait until your breast tissue has stabilized. This typically happens after puberty for teenagers and after hormonal changes have settled for adults.
-
The condition bothers you emotionally or physically: If enlarged breasts cause you significant distress, impacting your self-esteem, social life, or ability to participate in physical activities, surgery might be a good option.
-
Non-surgical methods haven’t been effective: If you’ve tried lifestyle changes like weight loss or exercise and they haven’t addressed the issue,surgery might be the next step.
-
You’re in good overall health: Having a healthy body weight and no major health conditions is important for undergoing any surgery.
-
You have realistic expectations: Surgery can improve your appearance and confidence, but it won’t create a perfectly symmetrical, sculpted chest. Discuss desired outcomes with your doctor.
Here’s when to consult a doctor right away:
-
You experience sudden or rapid breast enlargement.
-
You have pain or tenderness in your breasts.
-
You notice any discharge from your nipples.
Ultimately, the decision to get male breast reduction surgery is a personal one. Consulting with a board-certified plastic surgeon who specializes in male breast surgery is crucial. They can assess your situation, discuss treatment options, and help you decide if surgery is the right choice for you.

HOW DO I TELL IF MY GYNECOMASTIA IS CAUSED BY FAT OR BREAST TISSUES?
While there might be some overlap, there are some key differences between gynecomastia (breast tissue enlargement) and chest fat. Here’s how you can get a general idea, but it’s important to remember this isn’t a substitute for professional diagnosis:
Feel:
-
Gynecomastia: Feels firm or rubbery, potentially with a distinct lump under the skin.
-
Chest fat: Feels soft and similar to fat deposits elsewhere on your body.
Appearance:
-
Gynecomastia: Often has a rounder, more defined shape resembling female breasts. Nipples might be puffy or enlarged.
-
Chest fat: May appear saggy or droopy without a well-defined shape.
Weight:
-
Gynecomastia: Might not necessarily change significantly with weight loss.
-
Chest fat: Should at least partially reduce in size with weight loss efforts as it’s part of your overall body fat.
Here are some additional points to consider:
-
Age:Gynecomastia is more common during hormonal fluctuations like puberty or older adulthood.Weight gain can cause chest fat accumulation at any age.
-
Tenderness:Gynecomastia can sometimes cause tenderness or pain,while chest fat typically wouldn’t.
If you’re unsure about the cause of your enlarged chest tissue, it’s important to see a doctor.
A doctor can perform a physical examination, potentially order imaging tests like an ultrasound, and determine if you have gynecomastia or just excess chest fat. This helps ensure you get the most appropriate treatment course.

CAN I WAIT AND WATCH AND HOPE FOR MALE BREASTS TO DISAPPEAR IN DUE COURSE?
Whether you can wait and see if your male breasts (gynecomastia) disappear depends on several factors:
Your age:
-
Teenagers: If you’re a teenager going through puberty, waiting might be reasonable. Hormone fluctuations during puberty often cause gynecomastia, and it usually resolves on its own within 6 months to 2 years.
-
Adults: For adults, especially those with established gynecomastia, waiting might not be as effective. Testosterone levels naturally decline with age, and this can contribute to gynecomastia.
The cause:
-
If your gynecomastia is caused by an underlying medical condition, medication, or substance use, addressing the root cause is crucial. Waiting might not resolve the issue if the cause persists.
-
Severity: For mild gynecomastia that doesn’t cause significant emotional or physical distress, waiting might be an option. However, for more prominent cases impacting your self-esteem or daily activities, you might prefer a more definitive solution.
Here’s what to consider when deciding to wait and see:
-
Emotional wellbeing: If your enlarged breasts are causing anxiety, depression, or affecting your social life, waiting might not be the best option.
-
Physical discomfort: Pain or tenderness in your breasts can be a reason to seek medical attention sooner.
-
Underlying concerns: If you suspect an underlying medical condition, waiting could delay proper diagnosis and treatment.
It’s always best to consult a doctor. They can assess your situation, determine the cause of your gynecomastia, and discuss the pros and cons of waiting versus seeking treatment. Here are some benefits of getting a professional opinion:
-
Accurate diagnosis: The doctor can differentiate between gynecomastia and excess chest fat.
-
Identifying the cause: They can determine if there’s an underlying medical condition requiring treatment.
-
Treatment options: They can discuss various treatment options, including non-surgical approaches like weight loss or medication adjustments (if applicable), or surgical options if needed.
Ultimately, the decision to wait and see or seek treatment is a personal one. However, a doctor’s guidance can help you make an informed choice based on your specific circumstances.
ARE THERE ANY MEDICINES FOR CORRECTION OF MALE BREAST PROBLEM?
Yes, there are a few potential medication options for the treatment of gynecomastia, but it’s absolutely crucial to consult with a doctor to determine the underlying cause and the best course of action. Here’s what you need to know:
Understanding Gynecomastia Gynecomastia is the enlargement of breast tissue in males, often caused by an imbalance of the hormones estrogen and testosterone. It can have various causes, including:
-
Puberty: Hormonal shifts during puberty can sometimes cause temporary gynecomastia.
-
Medications: Certain medications, including those for prostate conditions, heart disease, and psychiatric conditions, can cause gynecomastia.
-
Health Conditions: Conditions like hypogonadism, liver disease, kidney disease, and some tumors can lead to gynecomastia.
Medication Options
-
Selective Estrogen Receptor Modulators (SERMs): Medications like tamoxifen and raloxifene can block the effects of estrogen on breast tissue. These are often prescribed for gynecomastia.
-
Testosterone Replacement Therapy (TRT): In cases where gynecomastia is caused by low testosterone levels, TRT may be recommended.
Important Considerations:
-
Not for everyone: Medications are not always suitable for treating gynecomastia. Your doctor will evaluate your individual situation.
-
Underlying causes: It’s vital to identify and treat any underlying health conditions that may be contributing to gynecomastia.Surgery: In some cases, surgery might be recommended to remove excess breast tissue.
Never Self-Medicate
Do not attempt to self-treat gynecomastia with any medication. Consult a doctor for proper diagnosis and to discuss the most appropriate treatment options.

WHEN CAN I START EXERCING AFTER MALE BREAST SURGERY?
The timeline for resuming exercise after male breast surgery (gynecomastia surgery) depends on several factors, including:
-
Type of surgery: The extent of your surgery and the techniques used will influence your recovery time.
-
Individual healing: Everyone heals at a different pace. Your surgeon will monitor your progress personally.
-
Pain and discomfort: Listen to your body and gradually increase activity as your pain levels decrease.
General Guidelines:
-
First few days: Rest is crucial. You may experience some pain and swelling. Light walking is encouraged to promote blood flow and prevent blood clots.
-
Weeks 1-2: You may be able to resume light cardio like brisk walking or using the elliptical. Avoid any exercise that strains your chest or upper body.
-
Weeks 3-4: If cleared by your surgeon, you might begin light weightlifting, focusing on your lower body. Continue with cardio workouts, gradually increasing intensity.
-
Weeks 4-6: As your incision sites heal, you might be able to reintroduce upper body strength training under your surgeon’s guidance. Start with light weights and fewer repetitions. Avoid any exercise that puts significant strain on the chest.
-
6+ weeks: With continued healing, you may be able to return to your usual workout routine gradually.
Absolutely Crucial:
-
Surgeon’s Instructions: Always follow your surgeon’s specific post-op instructions; they know your individual situation best.
-
Listen to your body: If you experience any pain, swelling, or discomfort, stop exercising and consult your surgeon.
-
Gradual return: Do not rush into your old routine. Start slowly and gradually increase the intensity and duration of your workouts.
Important Things to Avoid:
-
Contact sports: Avoid activities that increase the risk of chest impact.
-
Exercises that strain the chest: Avoid push-ups, bench presses, chest flies, or any exercises that strain the incision areas.
Remember, patience is essential for a successful recovery.
